|
Propulsion is not only a fundamental part for spacecraft and aviation, but also for the maritime environment since
it is responsible for giving the thrust and force necessary to move large structures in the sea.
WHAT IS MARINE PROPULSION?
It consists of a mechanical assembly and a propulsion device that contains an energy that will be transformed into a force. A propulsion unit consists of the machinery,
equipment and controls that can be mechanical, electrical or hydraulic connected to a propulsion shaft. The propeller is the typical propulsion element of the boats. Its
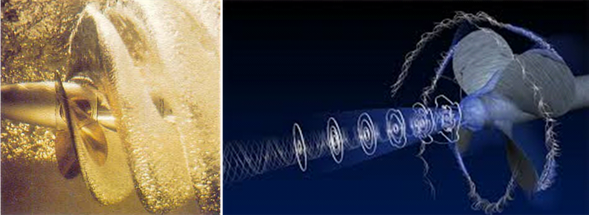
operation is based on the physical phenomenon of lift, where the movement of a propeller blade in a fluid, due to the action of the engine, generates a thrust on the
blade that can be used to produce the forward movement of the ship. Diesel engines have the same power forward as backward, being able to stop or reverse the direction of
propulsion almost immediately (quick response to the commands given) with normal shaft revolutions.
Engines

They carry out the transformation of the mechanical energy necessary to create the movement and the thrust force in the ship.
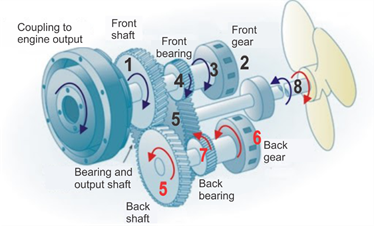
Reducing box
Their purpose is to reduce the revolutions produced by machines or engines, according to the efficiency of the propeller. Additionally, they couple and uncouple the motor
from the propeller shaft and reverse, in some cases, its direction of rotation according to the configuration of the propulsion unit and the type of vessel.
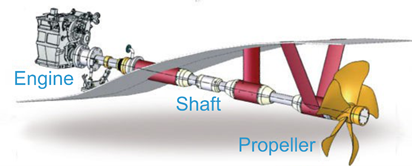
Propulsion shafts
They transmit the movement from the engine and reducers to the propeller along the ship; they are supported by bearings or rests, which provide the necessary support points
and absorb vibrations and axial and radial thrusts. Its length, diameter and type of bearings used are considered important.
Propellers
The main function of a propeller is to transform the mechanical energy delivered in the form of torque by the shafts into effective thrust. The most commonly used type of
propeller is the propeller, which generates thrust by giving speed to a column of water, which is displaced in the opposite direction to the movement of the ship.

Types of propulsion
Currently there are different types of propulsion systems, as well as their applications. Much research has been carried out to try to obtain the most efficient system
and to lower operating costs (fuel consumption), which many systems have managed to overcome in the maritime field due to the high performance of the ship, but we must
also consider the type of propulsion depending on which ship it is required for.
These are some of the most common types of propulsion.
Fixed, variable and controlled pitch propellers
In order to identify the types of pitch that propellers have, we must first know what the pitch of a propeller consists of. This is defined by the angles of the face of
the blades, that is, the greater the angle of the face of the blade, the greater the pitch. As each of the blades is attached to the shaft, the angle they determine is
fixed and indicates the speed at which it will advance (acceleration) and how far it will travel in each rotation (speed). We must consider that these effects are
inversely proportional to each other and the convenience points have to be determined for the boat to perform better. That is, if we are going to have a great
acceleration, we will have a limited maximum speed. Whereas, if we have a high maximum speed, we will accelerate moderately. The pitch in a propeller is classified as
fixed, variable and controlled.
· Fixed pitch propeller
The most common due to its relative “low cost” is the fixed pitch propeller. These propellers are also known as "constant pitch" which means that the pitch over the
entire surface of the blade (except blade angles) does not change. They are used in most commercial vessels such as tugboats, trawlers, fishing boats, etc. A fixed pitch
propeller is more efficient than a variable pitch propeller for a particular rotational speed and load and can transmit power more efficiently than a variable pitch
propeller. With another speed or load, the fixed pitch will not be the most efficient since the angle will not be optimal.

· Variable pitch propeller

As mentioned in the fixed pitch propeller, most propellers have a constant pitch, but there are some special applications (large ships or speed boats) where the need for
maximum possible efficiency is imperative. In these propellers the pitch can vary in each radius (depending on the design), but it is more common to find those where the
pitch is usually reduced near the tips to reduce the pressure of the blades and the possibility of cavitation. In this type of propeller its blades can rotate around a
long axis to change its angle of attack. If this angle can be set to negative values, the propeller can create a reversal of thrust for braking or reversing without
changing the direction of rotation of the shaft.
· Controllable pitch propeller

This system is commanded by a remote control from the bridge or from the engine control room, indistinctly, but it cannot be done simultaneously from both places. The
hydraulic pumps that generate this power are activated by electric engines that constantly rotate, passing the hydraulic fluid. Normally there are two, one in operation
and the other in reserve. They offer a great advantage in terms of cost of operation, but are much more expensive than fixed pitch.
Nozzles systems
Nozzles are used to increase propulsion performance, since they provide additional thrust. It is a system that modifies the speed of the water that attacks the propeller
and prevents the formation of swirls around the tips of the blades. As it passes through the nozzle the water undergoes an increase in speed causing a greater pressure
difference and providing an additional thrust. The application of this equipment is limited to low speed vessels (below 14 knots) such as trawlers, tugboats, dredgers,
etc.
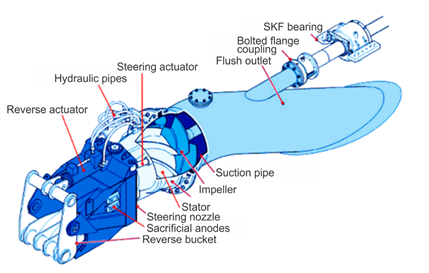
Azimutals
With this mechanism, the boat can be dynamically positioned or maintained in open water, allowing it to be in adverse weather positions. Its installation is flexible and
can be done in a small space. It consists of a modular construction with mechanical, hydraulic and electrical sub-assemblies that ensure a compact and flexible
installation, facilitating any subsequent maintenance work. It increases the maneuverability of the boat, giving it the possibility to turn 360° on its own length.
 Cycloidal Cycloidal
It is a highly maneuverable system, being able to change the direction of the thrust almost instantaneously. It is widely used in tugboats and ferries.
Water jets
It consists of a jet propulsion system. It generates propulsion by varying the amount of movement of the water that is forced towards the stern of the ship. It is used to
propel boats at speeds between approximately 25-40 knots, due to its great propulsive efficiency, good maneuverability, reduction of vibrations and the possibility of
retarding or reducing cavitation.
|