|
The mold is a cavity that is shaped like the part to be cast. Sand molding allows the manufacture of practically any geometry, which gives it a lot of versatility of use.
Sand casting is one of the most used processes in the foundry industry since most of the alloys can be cast in sand and allows the manufacture of very light parts up to very heavy pieces.
The most important parts for the construction of a foundry sand mold are: The pattern of the part to be obtained, the risering system and the gating system.

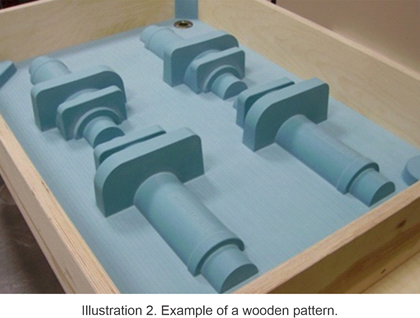
FOUNDRY PATTERN
It is a representation of the piece that you want to obtain in metal, it is slightly larger than the final piece and for its manufacture the shrinkage of the metal and the machining
tolerances are taken into consideration. The pattern can be made of wood, resins or soft metals.
The pattern is the base to make the sand mold, it can be a single piece or be composed of several parts. Around the pattern the mold is built using sand mixed with some binder
depending on the molding method. At the end of the mold, the pattern is removed, leaving a cavity in the sand in the shape of the pattern.
RISERING SYSTEM
It is a reserve in the mold that functions as a source of liquid metal to compensate for the shrinkage of the molten metal during solidification. This should be designed in
such a way that it is the last part of the mold to solidify. Also known as "Riser" or "Feeder".
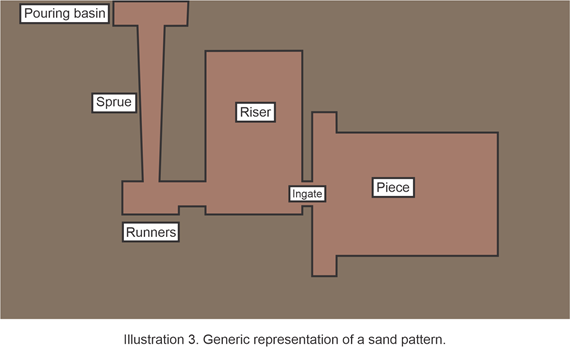
GATING SYSTEM
It is a network of channels through which the molten metal flows that connects from the filling point to the mold cavity.
Its main parts are:
- Pouring basin: It is located in the upper part of the drinker and serves to avoid splashes and air trapping during the entrance of the material to the drinker.
- Sprue: It is a vertical channel through which the molten metal enters.
- Runners: they are horizontal channels through which the metal flows towards the cavity of the part.
- Ingate: they are the access points of the molten metal to the part.
A good casting system is carried out considering that the metal enters with a laminar flow to avoid gas trapping and erosion of the mold walls, as well as providing liquid
metal at one or more ingates to the piece.
|